Running Robots From Your Browser With Cylon.js
Ever thought about controlling robots directly from your browser? With the latest release of Cylon.js, we make it easy to control robots and connected devices from your own browser-based and mobile applications.
For now, in-browser support is limited to a few modules, due to browser sandboxing. JS running in a normal browser can't, for instance, talk directly to Bluetooth or a serial port. You CAN however do this if you are running Cylon.js in a Chrome application.
However, if a Cylon.js browser communicates with hardware over the network, it will work from within any browser without a hitch.
For example, the cylon-ardrone, cylon-spark, cylon-leapmotion, cylon-hue and more are supported already.
In this example, we're going to blink the LED on a Spark Core from Cylon.js running in a regular browser.
Create
In a new folder, use NPM to install cylon-spark:
$ npm install cylon cylon-spark
Once that's installed copy this Cylon.js program to script.js.
Add your Spark Core's accessToken and deviceId.
You can get both of these from Spark's Build tool:
-
accessToken: In the Build tool, click on the Settings cog in the bottom-left corner to find your access token. -
deviceId: After you have your Spark Core registered to your account through the Tinker app, click on the Cores section (just above the Settings cog) on the Build tool. Then, click on the arrow next to your core's name to get its device ID.
Make sure to add these to the script, or it won't work.
var Cylon = require('cylon'); Cylon.robot({ connections: { spark: { adaptor: 'spark', accessToken: '[YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN]', deviceId: '[YOUR_DEVICE_ID]' } }, devices: { led: { driver: 'led', pin: 'D7' } }, work: function(my) { every((1).second(), function() { my.led.toggle(); }); } }).start();
Code in place, let's write a small HTML file (index.html) that'll host the script:
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> </head> <body> <script src="browser_script.js"></script> </body> </html>
And that's it.
Compile
Now with the pieces in place, let's compile the Cylon.js program for browser use with the Browserify tool.
If you don't have it already, install it through NPM:
$ npm install -g browserify
Then, use it to compile the script:
$ browserify script.js -r cylon-gpio -r cylon-spark -o browser_script.js
Run
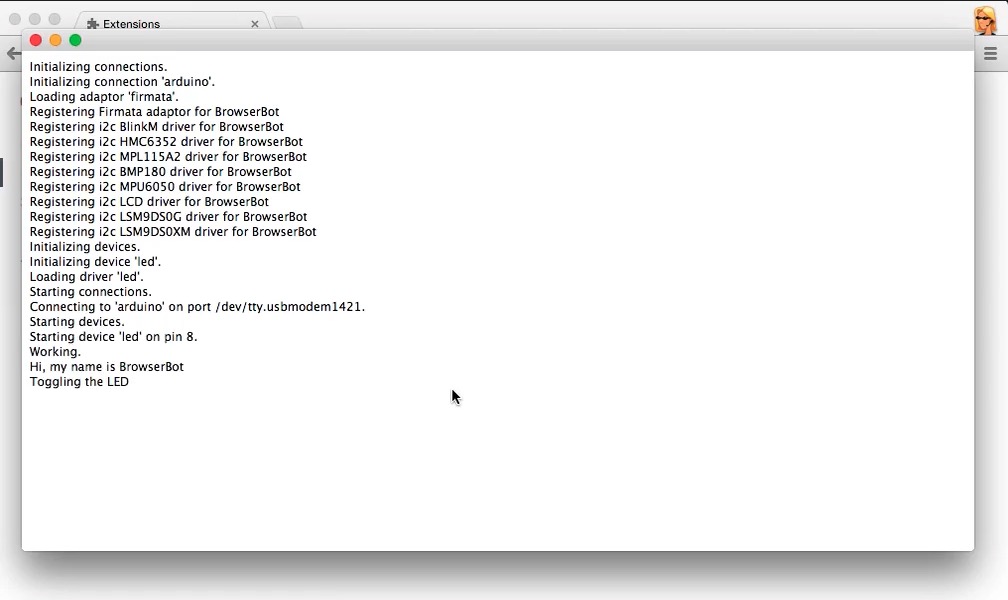
Now, just open index.html in your browser and your Spark's LED should start blinking.
Want more?
From here, the sky's the limit. If you want to get started on a more complex Cylon.js robot for use in the browser, we've created an example project on GitHub to get you started.
If that's not enough for you, you can also package Cylon.js scripts into Chrome Apps. We've created another example project repo to get you started on that front.

You can even include Cylon.js in your PhoneGap mobile app. Look for an upcoming blog post focusing on this, but for now here is an example of PhoneGap + Cylon.js
Check out our Browser Support guide for more information.
For more updates, be sure to follow us on Twitter at @CylonJS.
Posts
- Cylon.js Off And Rolling In 2016
- Cylon.js 1.2.0 - Logging and Timing and BLE! Oh my!
- Cylon.js 1.1.0 - The Big Cleanup
- Hello, Node Bebop Drone
- Cylon.js featured in Wired
- Cylon.js 1.0.0 is here!
- Using Socket.io With The Cylon.js API
- Cylon 0.22.0 - A New Year's Release
- Cylon 0.21.0 is out!
- Creating Multiplatform Precompiled Binaries for Node.js Modules
- Cylon 0.20.0 is out!
- Running Robots From Your Browser With Cylon.js
- Winning the Dreamforce 500 With Cylon.js
- With The New Cylon.js 0.19.0, You Can Be Fluent Too
- Cylon.js on Intel Edison
- Cylon Takes Off on NodeBots Day
- Cylon.js Fun With The Arduino Yun
- Control Robots From Your Pebble
- Making Moves With Intel Galileo
- The Cylon Nest
- Announcing Full Tessel Support!
- Cylon 0.15.0 is Out!
- Cylon.js in Make Magazine!
- Cylon.js At JSConf 2014
- Cylon.js Takes The Stage At MakerFaire
- Cylon.js In Scotland
- Robots Are The New Normal At NextBerlin
- Thingscon - Ich Bin Ein Cylon
- National Robotics Week at the Robotics Society of Southern California
- Functional Robots With Wisp
- Release 0.12 Is For RobotOps
- Making Waves At Makerland
- This One Goes To 0.11 Of Pure JavaScript
- Tipping SCaLE12X
- Intro Robeaux- A Universal User Interface To Robotic Devices
- ng-robots! A Fun Robot Hackathon At The First ng-conf
- Number 9! The Release In Which We Add A Web UX, More Platforms, and Tools
- Release 0.8.0 Makes 10 Platforms
- RobotsConf Was Remarkable
- Dreamforce Means Connected Devices Are A Thing
- Dreamforce Is Coming!
- Welcome, Cylon.js