BeagleBone

Repository| Issues
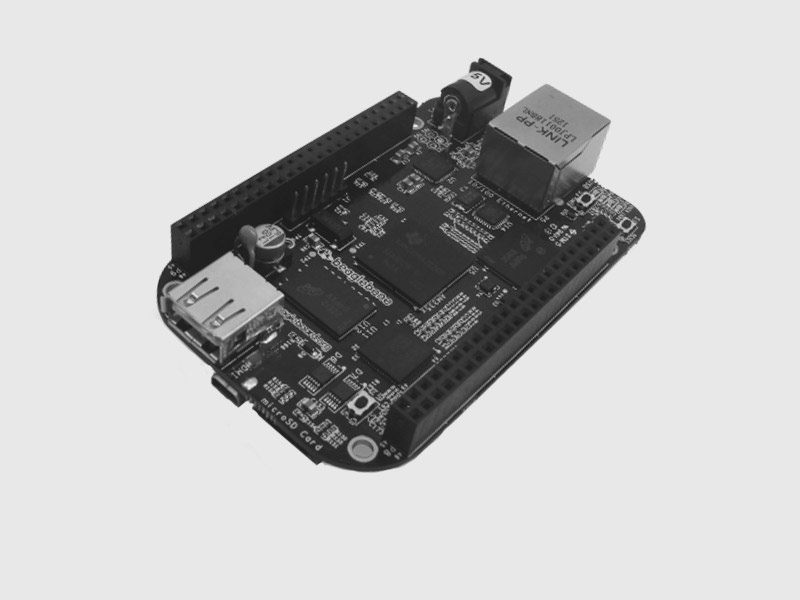
The BeagleBone Black is an ARM based single-board Linux computer, with many different GPIO interfaces built in.
For more info about the BeagleBone platform click here.
How to Install
Installing Cylon.js for the BeagleBone Black is pretty easy, but must be done on the Beaglebone Black itself, or on another Linux computer. Due to I2C device support, the module cannot be installed on OS X or Windows.
$ npm install cylon cylon-beaglebone
How to Use
var Cylon = require('cylon'); // Initialize the robot Cylon.robot({ connections: { beaglebone: { adaptor: 'beaglebone' } }, devices: { led: { driver: 'led', pin: 'P9_12' }, button: { driver: 'button', pin: 'P9_14' } }, work: function(my) { my.button.on('push', function() {my.led.toggle()}); } }).start();
How to Connect
You will likely want to connect your development machine to your BeagleBone Black while working on your code. You can do this easily, just by connecting to the BeagleBone Black over USB. Then, you can connect to the BBB using Network-Over-USB, and upload driver or configuration changes.
Important Note About Voltages
The Beaglebone Black is a 3.3V device. You will need a logic level converter to work with 5V devices, such as this one from SparkFun or this one from Adafruit.
Furthermore, the Analog to Digital Converters (ADC) cannot handle more than 1.8V input, so keep this in mind when connecting to analog devices, or risk burning up your BBB.
OS X
For OS X, some drivers need to be installed to allow Network-Over-USB access to the BeagleBone black. You can find the instructions on the BeagleBone site's getting started page.
Once you've installed the drivers and connected to the BeagleBone over USB, you can just SSH into it.
The BBB should have an IP address of 192.168.7.2.
Linux
For Linux machines, you will need to create a udev rule. You can find the instructions on the BeagleBone site's getting started page.
To connect to the BeagleBone Black from your Linux machine, save this script as bbb.sh (or whatever name you'd prefer).
Executing the script will then SSH into the BBB.
#!/bin/bash sudo -- sh -c 'echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward' sudo iptables -A POSTROUTING -t nat -j MASQUERADE ssh [email protected]
Windows
For Windows, some drivers need to be installed to allow Network-Over-USB access to the BeagleBone black. You can find the instructions on the BeagleBone site's getting started page.
The connection process for Windows is a bit more involved. But when you're done, it should be just as simple to connect to the board.
- First, follow this guide for setting up Internet Sharing on your Windows computer
- Next, install PuTTY (or your preferred SSH client) to SSH into the BeagleBone Black
- Finally, SSH into the BBB. It will have the same IP address (
192.168.7.2)
Credentials
By default, the BeagleBone's login credentials are:
-
user:
root - pass: none
Creating a BeagleBone Black SD Card with Debian
You may need to create a bootable SD card with the BBB Debian Linux distro.
Finding the SD Card's Name
OS X
To find the name of the SD card on OS X, use the diskutil command:
$ diskutil list /dev/disk0 #: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER 0: GUID_partition_scheme *500.3 GB disk0 1: EFI EFI 209.7 MB disk0s1 2: Apple_HFS Macintosh HD 499.4 GB disk0s2 3: Apple_Boot Recovery HD 650.0 MB disk0s3 /dev/disk1 #: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER 0: FDisk_partition_scheme *15.9 GB disk1 1: DOS_FAT_32 UNTITLED 15.9 GB disk1s1
In this case, the SD card's name is /dev/disk1.
Before you proceed, be sure to eject the mounted volume:
$ diskutil umount /dev/disk1s1
Linux
On most Linux distros, the df -h command should help you determine the name of your SD card.
Downloading the Linux Image, Flashing the SD Card
The image we're using is the official modified Debian distro provided by BeagleBoard, so we'll download it directly from them: http://debian.beagleboard.org/images/bone-debian-7.8-lxde-4gb-armhf-2015-03-01-4gb.img.xz.
Once the image has downloaded, uncompress it like this:
unxz bone-debian-7.8-lxde-4gb-armhf-2015-03-01-4gb.img.xz
The final step is to flash the image onto the SD card.
You can do so by running this command (be sure to update the of section to point to the SD card name you found earlier!):
$ sudo dd bs=1M if=./bone-debian-7.8-lxde-4gb-armhf-2015-03-01-4gb.img of=/dev/sdb && sudo sync
Booting Off Of The SD Card
Insert SD card into your (powered-down) board, hold down the USER/BOOT button (if using Black) and apply power, either by the USB cable or 5V adapter.
Configuring the BeagleBone Black
After SSHing into the BeagleBone Black, save the following script into ~/profile.
Be sure to do this on the BBB.
This will allow your BeagleBone Black to share your computer's internet connection.
#!/bin/bash
ROUTE=`route | grep 0.0.0.0 | wc -l`
if [ $ROUTE -eq 0 ]
then
sudo -- sh -c 'echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" >> /etc/resolv.conf'
sudo /sbin/route add default gw 192.168.7.1
ping www.google.com -q -c2 > /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
sudo ntpdate ntp.ubuntu.com
fi
fi
After the script is saved, it will automatically run when the BeagleBone Black boots, so you only have to do this step once.
Resizing the SD Card Partition
At this point, we have a full Debian Linux OS set up, and can connect over SSH to the BBB. Now, we need to adjust the SD card's partitions, to give us space to install dependencies and do some work.
First, login to the board over SSH, and run this series of commands:
$ fdisk /dev/mmcblk0 d 2 n p 2 w $ shutdown -r now
After the board finishes restarting, log back in and resize the filesystem on the SD card before another restart:
$ resize2fs /dev/mmcblk0p2 $ shutdown -r now
After this restart has completed, log back in, and check the partition has been correctly resized:
$ df -h
The /dev/root partition should take up the entire size of the SD card.
With this done, we're now ready to start running Cylon directly on the BeagleBone Black.
Drivers
All Cylon.js Digital, Analog & PWM GPIO drivers, as well as i2c drivers listed below should work with the BeagleBone: