Connect Intel Edison To AT&T M2X In 60 Lines Of JavaScript
Welcome! In this workshop, we're going to show you how to create a AT&T M2X connected device, using the brand new Intel Edison, in 60 lines of JavaScript. Plus we're going to have some fun too.
Getting Started
- You need an Intel Edison with Arduino Breakout Board, 2 USB Cables, and a Grove Starter Kit to participate in this workshop.
- Platform instructions
- Windows installation instructions
- Mac OSX installation instructions
- Linux installation instructions
- Take note of the IP address for your Intel Edison
- You will need to install the Intel XDK (Cross-platform Developer Kit) IoT Edition
- Get started by running the "Intel XDK IoT Edition" program.
- The dialog "Please log into Intel XDK" will be displayed. You will need to register for an account, or else sign in using your existing Intel XDK account, if you have one.
- That is it, now you are ready to get going!
Create a Blank Project
- First, we need to create a new project. Choose "New Project".
- Click on "Start With A Sample Or Template" in the "Internet Of Things (IoT) with Node.js Projects.
- Click on "Blank Template", and then click on "Use This Template".
- Enter in a name for this project, such as "hw15", then click on the "Create" button.
-
Click on the file named "package.json". The file will open in the XDK editor. Copy the following code, and paste into your editor, replacing all of the code already in the "package.json" file:
package.json
{ "name": "blankapp", "description": "", "version": "0.0.1", "main": "main.js", "engines": { "node": ">=0.10.0" }, "dependencies": { "cylon-intel-iot": "*" } } - You will need to connect to your Edison board from your computer to send code to it. Choose the "Add Manual Connection" from the "IoT Device" menu located at the bottom right. Enter the IP address for the your Edison, and "58888" for the Port. Click on the "Connect" button to save your connection.
Blinking LED
Let's start with the 'Hello, World' of the Internet of Things: making an LED blink.
-
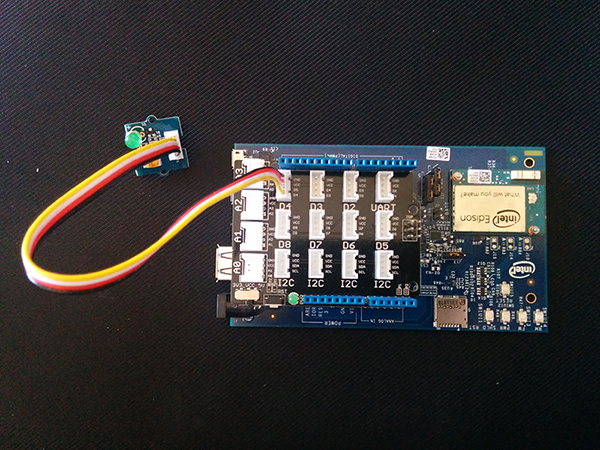
Plug the LED that is included with the Grove Starter Kit into the jack labeled 'D4', like this:
-
Enter the following code into the Intel XDK editor into the file named "main.js", replacing everything in the file:
main.js
var Cylon = require('cylon'); Cylon.robot({ connections: { edison: { adaptor: 'intel-iot' } }, devices: { led: { driver: 'led', pin: 4, connection: 'edison' } }, work: function(my) { setInterval(function() { my.led.toggle(); }, 1000); } }).start();
-
Click on the "Install/Build" icon located at the bottom of the XDK editor. This will install the needed Cylon.js software on the Edison, as well as copying your code.
-
Now, click on the "Run" icon located at the bottom of the XDK editor.
The Cylon.js program will execute on the Edison itself, and will make the LED turn on/off every second.
LCD + Temp Sensor + LED
Now, let's add a temperature sensor and LCD screen, so you can see the ambient room temperature and display it on the screen.
-
Leave the LED plugged in, and plug in the temperature sensor that is included with the Grove Starter Kit, into the jack labeled 'A3', like this:
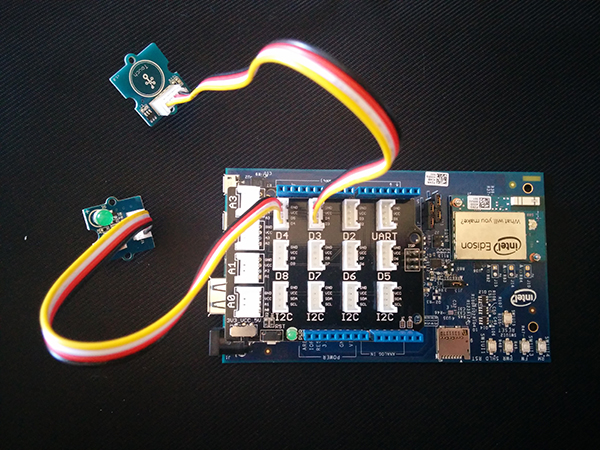
-
And the LCD into the jack labeled 'I2C', like this:

-
Now, enter this code into the Intel XDK editor for the file "main.js", replacing everything:
main.js
var Cylon = require('cylon'); Cylon.robot({ connections: { edison: { adaptor: 'intel-iot' } }, devices: { led: { driver: 'led', pin: 4}, sensor: { driver: 'upm-grovetemp', pin: 0}, screen: { driver: 'upm-jhd1313m1'} }, work: function(my) { my.screen.setColor(255,0,0); setInterval(function() { my.led.turnOn() setTimeout(function() { my.led.turnOff(); }, 300); my.screen.setCursor(0,0); my.screen.write(my.sensor.value().toString() + "C"); }, 2000); } }).start();
-
Click on the "Run" icon located at the bottom of the XDK editor.
Once the program is running, you should see the temperature displayed on the LCD and the LED will light up whenever a new sample is recorded.
Create an ATT M2X application
Let's throw m2x into the mix!
- First navigate to m2x signup and create a new account.
- Create a new device with the name "Edison" and "Private" visibility.
- Select the newly created "Edison" device and add a new stream
- StremID "temp"
- Unit "celsius"
- Save the new stream
- Take note of your "Device ID"
- Navigate to the Master Key page and take note of your "Master Key"
ATT M2X + LCD + Temp Sensor + LED
Now, we're ready to connect our device to ATT M2X. Leave the temp sensor, LCD and LED plugged in. All we will need is to change the Cylon.js program to connect our device to the AT&T M2X APIs.
-
Enter this code into the Intel XDK editor, replacing all of the previous code in the "main.js" file:
main.js
var Cylon = require('cylon'); Cylon.robot({ connections: { edison: { adaptor: "intel-iot" }, m2x: { adaptor: "m2x", masterKey: "<masterKey>" } }, devices: { led: { driver: 'led', pin: 4 }, sensor: { driver: 'upm-grovetemp', pin: 0 }, screen: { driver: 'upm-jhd1313m1' }, m2x: { driver: "m2x", id: "<deviceId>", connection: "m2x" } }, work: function(my) { my.screen.setColor(255,0,0); my.m2x.subscribe("temp", { interval: 1000 }); my.m2x.on("error", function(err) { console.log("m2x error: ", err); }); my.m2x.on("temp", function(data) { if (data.values.length > 0) { my.screen.setCursor(0,0); my.screen.write(data.values[0].value.toString() + "C"); } }); setInterval(function() { my.led.turnOn(); my.m2x.publish("temp", my.sensor.value(), function(err) { my.led.turnOff(); if (err) { console.log("err: ", err); } }); }, 2000); } }).start();
-
At the top of the "main.js" file, change the "masterKey" and "deviceId" located at line 3 and 4 to the AT&T M2X info that matches your device.
-
You will need to add the "cylon-m2x" module to your "package.json" as well. Replace the entire file's contents with this code:
package.json
{ "name": "blankapp", "description": "", "version": "0.0.1", "main": "main.js", "engines": { "node": ">=0.10.0" }, "dependencies": { "cylon-intel-iot": "*", "cylon-m2x": "*" } } -
Click on the "Run" icon located at the bottom of the XDK editor.
Once the program is running, the LED will light up while the Edison communcates with the AT&T M2X cloud, and then displays the new temp on the LCD, when the M2X API sends an update to the device.
Wrap Up
That concludes this workshop. You've just connected the Intel Edison to 3 different devices and the AT&T M2X API. Great job!