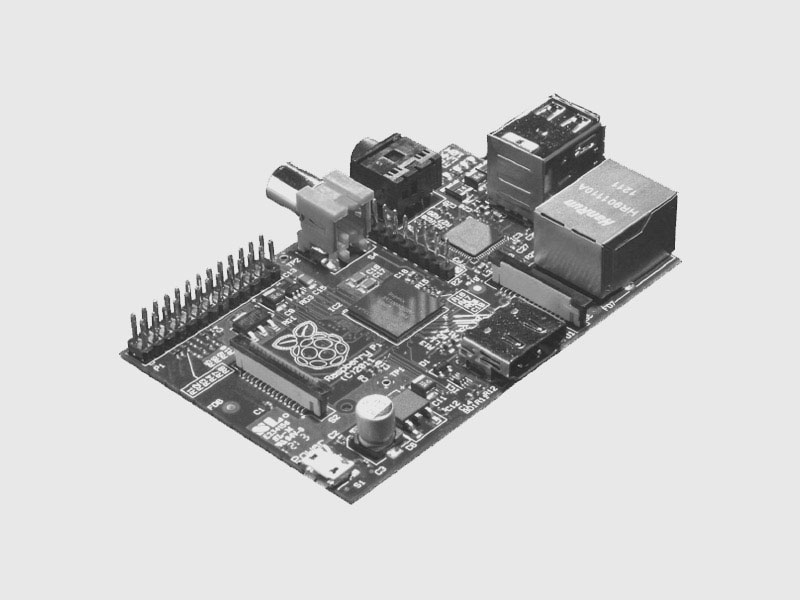
Raspberry Pi

Repository| Issues
The Raspberry Pi is an inexpensive and popular ARM based single board computer with digital & PWM GPIO, and i2c interfaces built in.
The Raspberry Pi is a credit-card-sized single-board computer developed in the UK by the Raspberry Pi Foundation with the intention of promoting the teaching of basic computer science in schools
For more info about the Raspberry Pi platform, click here.
How to Install
Installing Cylon.js for the Raspberry Pi is easy, but must be done on the Raspi itself, or on another Linux computer. Due to I2C device support, the module cannot be installed on OS X or Windows.
Install the module with:
$ npm install cylon cylon-raspi
How to Use
This small program causes an LED to blink.
var Cylon = require("cylon"); Cylon.robot({ connections: { raspi: { adaptor: 'raspi' } }, devices: { led: { driver: 'led', pin: 11 } }, work: function(my) { every((1).second(), my.led.toggle); } }).start();
How to Connect
Install the lastest Raspbian OS
You can get it from here: http://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/
Setting the Raspberry Pi keyboard
Having trouble with your Raspberry Pi keyboard layout? Use the following command:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure keyboard-configuration
Update your Raspbian and install Node.js
These commands need to be run after SSHing into the Raspi:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade wget http://nodejs.org/dist/v0.10.28/node-v0.10.28-linux-arm-pi.tar.gz tar -xvzf node-v0.10.28-linux-arm-pi.tar.gz node-v0.10.28-linux-arm-pi/bin/node --version
You should see the node version you just installed.
$ node --version v0.10.28
Once you have installed Node.js, you need to add the following to your ~/.bash_profile file. Create this file if it does not already exist, and add this to it:
NODE_JS_HOME=/home/pi/node-v0.10.28-linux-arm-pi PATH=$PATH:$NODE_JS_HOME/bin
This will setup the path for you every time you login. Run the source ~/.bash_profile command to load it right now without having to login again.
Thanks @joshmarinacci for the blog post at http://joshondesign.com/2013/10/23/noderpi where these modified instructions were taken.
Connecting to Raspberry Pi GPIO
This module only works on a real Raspberry Pi. Do not bother trying on any other kind of computer, it will not work. Also note you will need to connect actual circuits to the Raspberry Pi's GPIO pins.
In order to access the GPIO pins without using sudo you will need to both app the pi user to the gpio group:
sudo usermod -G gpio pi
And also add the following udev rules file to /etc/udev/rules.d/91-gpio.rules:
SUBSYSTEM=="gpio", KERNEL=="gpiochip*", ACTION=="add", PROGRAM="/bin/sh -c 'chown root:gpio /sys/class/gpio/export /sys/class/gpio/unexport ; chmod 220 /sys/class/gpio/export /sys/class/gpio/unexport'" SUBSYSTEM=="gpio", KERNEL=="gpio*", ACTION=="add", PROGRAM="/bin/sh -c 'chown root:gpio /sys%p/active_low /sys%p/direction /sys%p/edge /sys%p/value ; chmod 660 /sys%p/active_low /sys%p/direction /sys%p/edge /sys%p/value'"
Thanks to "MikeDK" for the above solution: https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?p=198148#p198148
Enabling the Raspberry Pi i2c on Raspbian
You must add these two entries to your /etc/modules
i2c-bcm2708 i2c-dev
You must also ensure that these entries are commented in your /etc/modprobe.d/raspi-blacklist.conf
#blacklist spi-bcm2708 #blacklist i2c-bcm2708
You will also need to update the /boot/config.txt file. Edit it add the following text:
dtparam=i2c1=on dtparam=i2c_arm=on
Finally, you need to allow the pi user permissions to access the i2c interface by running this command:
sudo usermod -G i2c pi
Now restart your Raspberry Pi.
Enabling PWM output on GPIO pins.
You need to install and have pi-blaster running in the raspberry-pi, you can follow the instructions for pi-blaster install in the pi-blaster repo here:
https://github.com/sarfata/pi-blaster
Available PINS
The following object depicts available pins for all revisions of raspberry-pi, the key is the actual number of the physical pin header on the board,the value is the GPIO pin number assigned by the OS, for the pins with changes between board revisions, the value contains the variations of GPIO pin number assignment between them (eg.rev1, rev2, rev3).
You should just be concerned with the key (number of the physical pin header on the board), Cylon.JS takes care of the board revision and GPIO pin numbers for you, this full list is for reference only.
PINS = {
3: {
rev1: 0,
rev2: 2,
rev3: 2
},
5: {
rev1: 1,
rev2: 3,
rev3: 3
},
7: 4,
8: 14,
10: 15,
11: 17,
12: 18,
13: {
rev1: 21,
rev2: 27,
rev3: 27
},
15: 22,
16: 23,
18: 24,
19: 10,
21: 9,
22: 25,
23: 11,
24: 8,
29: {
rev3: 5
},
31: {
rev3: 6
},
32: {
rev3: 12
},
33: {
rev3: 13
},
35: {
rev3: 19
},
36: {
rev3: 16
},
37: {
rev3: 26
},
38: {
rev3: 20
},
40: {
rev3: 21
}
};
The website http://pi.gadgetoid.com/pinout has a great visual representation of this information.
Drivers
All Cylon.js digital and PWM GPIO drivers listed below should work with the Raspberry Pi: